Meaning of Office Resources:
There are several elements without which an office cannot function properly. These elements are called office resources. In this article, we will discuss in detail regarding office resources.
We know the office is established to carry out various activities to achieve the organization's goals. Money, furniture, machines, vehicles, communication means, human resources, and so on are required for the establishment and smooth operation. The office needs more efficient things and human resources to function correctly to achieve the organizational goal. These requirements are called office resources.
To summarize, office resources include all things and materials, as well as human resources (also known as office personnel), that are used for establishing, operating, and achieving organizational goals. Office resources include human resources, finance, materials and supplies, communication channels, and transportation. Human resources are only one type of resource that can effectively mobilize others. To support human resources, other physical resources are required.
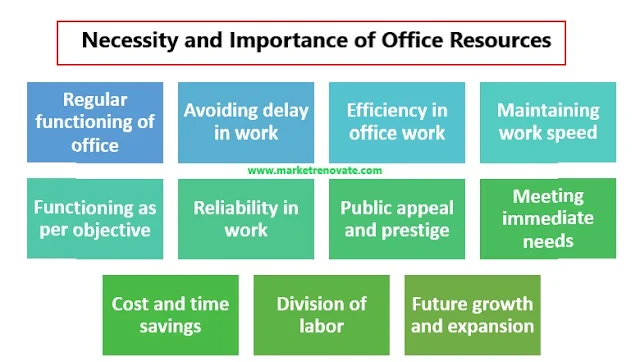
Necessity and Importance of Office Resources
It is only possible to imagine establishing and running an office with resources. However, on the other hand, an office without resources is analogous to the human body's skeleton. So, office resources are essential for the smooth operation of the office. The necessity and significance of office resources are examined in this section under the following headings:
(i) Regular functioning of office: To carry out official activities smoothly and consistently, office resources are required. Office resources, such as all physical materials and human resources, enable an organization to achieve its goals. The absence of any single office resource may cause an imbalance in the office's operations.
(ii) Avoiding delay in work: The absence of any required resource causes work to be delayed. As a result, an office should be well equipped with all necessary resources, such as men, machines, materials, money, and so on, to avoid work delays.
(iii) Efficiency in office work: The office resources aid in the practical, timely, and efficient performance of official duties. A well-equipped office ensures that work is completed promptly, effectively, and qualitatively. Work efficiency boosts productivity, lowers costs, and saves time and effort.
(iv) Maintaining work speed: Official tasks must be finished on time. Therefore, it should maintain the expected work speed to complete various official tasks on time. Thus, modern office resources increase productivity and help to complete tasks on time. For example, calculators and computers can quickly and easily prepare numerical activities and financial statements.
(v) Functioning as per objective: Every organization is founded with a specific objective, goal, or target in mind. An office develops plans and policies to achieve such a goal. Then, with the availability of resources, it is possible to carry out the plan. Hence, office resources aid in the achievement of goals.
(vi) Reliability in work: A variety of official jobs are carried out using various resources, such as equipment, tools, and machinery. Work done with such resources is more reliable than work done manually. Conversely, works performed without such resources will be unreliable, and such works must be checked numerous times, which takes time. Work can thus be completed more accurately and confidently by utilizing various available resources.
(vii) Public appeal and prestige: Providing necessary resources improves work quality, which raises an organization's prestige. Having enough resources for official work improves accuracy and reliability. In addition, it fosters public trust and confidence in the direction of employee inspiration and attraction, thereby increasing morale and productivity.
(viii) Meeting immediate needs: Because an office should collect and maintain a minimum stock of required materials and supplies, resources required by an office can be met immediately. Conversely, if there are insufficient resources, the office will face numerous problems because it is challenging to manage immediately.
(ix) Cost and time savings: A fully equipped office with office resources can save money and time in running an office. Jobs are completed on time as long as they are planned and organized. When there is the proper division of labor, efficiency in operations, and high employee morale, costs are reduced, and valuable time is saved.
(x) Division of labor: Simply put, division of labor means breaking down a service process into its most minor independent steps. A well-equipped office can afford to have a division of labor. As a result, the division of labor aids in increasing office productivity. It also lowers the skills required by workers, saving money on training and development.
(xi) Future growth and expansion: Office resources assist the organization or institution in preparing for future growth and expansion. It is also an essential component in achieving the company's goal.
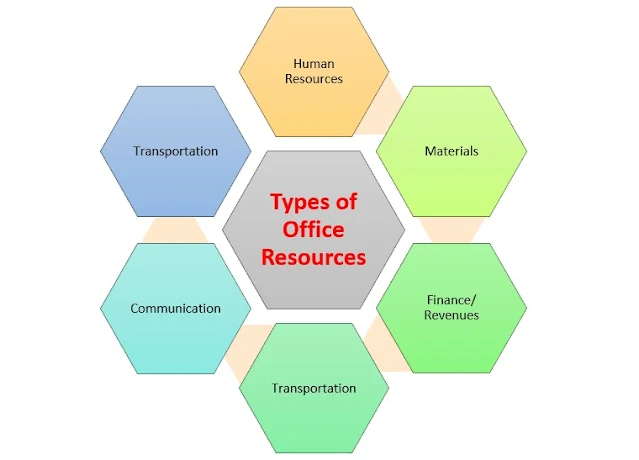
Types of Office Resources
Every office relies on a variety of resources to run smoothly. All commonly used resources are classified into the following types:
A. Human Resources
To carry out organizational tasks, the office requires several employees. The office appoints personnel at various levels based on the nature and volume of financial capacity. These individuals may have varying qualifications, skills, and abilities. Human resources are all the people who work in the office, from the lowest to the highest levels, to achieve organizational goals. In other words, all employees, from peon to chief, are referred to as human resources. It is the only existing resource capable of mobilizing additional resources. Other resources will be rendered ineffective in the absence of human resources. Other resources merely supplement human resources.
Human resource requirements are estimated based on the volume of work and through budgeting, known as 'darbandi' in Nepali. A sufficient number of human resources should be employed to ensure the smooth operation of the office. Over and understaffing in the office harms office job performance. Therefore, when dividing labor, the personnel management principle of 'the right person in the right place' should be followed, taking into account the ability, skill, and experience of the people involved.
Types of human resources
Human resources are classified into two types based on their knowledge, academic qualifications, ability, and skill:
(1) Technical human resource:
Technical human resources are employees with specialized technical knowledge in a specific field, such as medicine, surveying, designing, or teaching. Teachers, doctors, and lawyers are examples of such human resources.
The technical human resource may further be divided into the following types:
(a) Skilled human resources: Skilled human resources are people who have specialized technical knowledge in their field. As a result, they carry out their responsibilities on their own.
(b) Semi-skilled human resource: Semi-skilled human resources have some technical knowledge in their field. They are appointed to assist skilled human resources. They carry out tasks as directed by skilled human resources.
(c) Unskilled human resources: Unskilled human resources are individuals who work in a technical field but lack sufficient knowledge of the subject matter. They merely assist skilled and semi-skilled human resources.
(2) Administrative Human Resources:
Administrative Human Resources refer to all employees who work in the office daily in the administration and management fields. They are in charge of managerial and clerical tasks in the office, such as planning, policy development, decision-making, filing, communicating, record keeping, and so on. Such employees need specialized technical knowledge. Administrative and human resources include managers, section officers, and assistants.
Development of human resource
As previously stated, the organization's success relies heavily on its employees' performance. As a result, the office requires efficient and capable human resources. The office organizes various training, seminars, and workshops to help employees improve their abilities and skills. As a result, the office receives improved performance from them. Staff will be liabilities to the organization if they do not get a chance to engage in skill development programs.
In addition, the office needs to be able to inspire its workers to work toward its goals. Human resources are the only existing resource with sentiments, goals, and desires. It is not compatible with other resources. Therefore, the office must act appropriately toward the staff. They should be given numerous money, non-monetary lives, and other facilitators to motivate them. Among the motivating factors is timely payment of salaries and wages, the availability of allowances, medical services, bonuses, gratuities, and leaves of absence, as well as opportunities for career advancement, promotions, and rewards. All staff will give their best effort in return if the office manages these. As a result, the office is now operationally efficient, and the organizational objective can be accomplished.
B. Materials
The office needs a variety of supplies and items to run daily. More than human resources are needed to make things run smoothly. These tools and materials make the work reliable and comfortable. They are the inputs needed to run the office daily.
Durable and stationery materials are the two categories that are separated based on how long they are used. Durable materials are those goods and items typically used for more than a year. Examples include things like buildings, machinery, and furniture. The term "stationery material refers to products and items like chalk, stitch pins, and papers used within a year. Pens, paper, ribbons, files, and other stationary items are a few examples. To ensure the organization runs smoothly, the office must have enough materials.
C. Finance/ Revenues
We must start an organization with the necessary office resources known as finances and revenues. The terms "revenue" or "finance" refers to any organization's capital and source of income. The organization can only have sound management with modern equipment, efficient communication and transportation systems, and qualified and skilled human resources. Any organization is supposed to depend on it like blood. Therefore, it needs to be distributed to all organizational units.
Depending on the type of organization, finance varies. For instance, the initial source of income for any private business office is capital, followed by sales of goods and services. Social organizations receive funding from member dues, government grants, subsidies, and donations. Schools and colleges collect students' fees as a source of income. The government prepares the annual budget after collecting taxes, grants and aid from abroad, internal and external loans, and other forms of income. Estimating annual revenue from various sources and expenses under various headings is what is meant by an annual budget.
D. Transportation
The office transports its employees using a variety of vehicles as they must travel to various locations for business purposes. Similar to how people must bring and send people, things, and goods. The office uses a variety of modes of transportation for all these purposes, including bicycles, motorcycles, cars, jeeps, buses, trucks, ships, and horses. The use of transportation facilitates the quick and easy completion of official tasks. As a result, every office offers and encourages staff to use transportation services, considering both the need and the office's financial capacity. In its simplest form, transportation is the act of moving objects and people from one location to another using various methods.
Types and means of transport:
Offices use a variety of modes and types of transportation. Therefore, it may change depending on the office's geographical and economic circumstances, which are covered below:
(i) Land transportation:
Land transportation is moving people and things from one location to another via land or a road. Land transportation methods include trains, buses, trucks, jeeps, cars, motorcycles, bicycles, horses, and men. It is the most popular mode of transportation because it is significantly less expensive than all other options.
(ii) Water transportation:
Moving people and goods over bodies of water, such as rivers, seas, and oceans, are known as water transportation. Boats, ships, and other vessels are used for water transportation. It is less well known in Nepal because it is a landlocked country.
(iii) Air transportation:
Air transportation is moving people and cargo between locations via an air route. The vehicles used for air travel include airplanes, helicopters, hot air balloons, drones, and more. Due to the uneven development of land transportation across our nation, it is the most practical form of transportation. Therefore, with each passing day, its popularity grows. As a result, Nepal sees the establishment of numerous airline companies.
E. Communication
Communication refers to exchanging information, opinions, and experiences between individuals, whether orally or in writing. The office communicates via various channels, including the phone, e-mail, internet, fax, and letters.
Communication is a critical component of office administrative processes. Through communication, management conveys its plans and policies, establishes order, gives orders, etc., to lower-level employees. The lower-level staff uses the same communication channels to pass along issues, situational information, suggestions, etc. In addition, the office uses it to gather helpful information and stay in touch with various parties like debtors, creditors, banks, etc.
Types of communication:
Communication can be divided into two types, as shown below:
(i) Internal communication:
Internal communication refers to exchanging information between and among members of the same organization. The employees of various departments or sections converse with one another in this manner. For example, this type of communication includes interactions between account and marketing department employees within the same company. In general, management uses internal communication to share plans, policies, decisions, direction, etc., with its staff and departments and to gather issues, recommendations, successes, feedback, etc. from them. Examples of internal communication include circulars, memos, resolutions, notices, manuals, and bulletins, among others.
(ii) External communication:
External communication is the process by which different organizations, whether domestic or foreign, exchange information, opinions, ideas, and experience. Formal written/oral/verbal communication conducted with the outside world is called external communication. However, most communication today occurs over electronic channels like the internet, fax, and telex. External communication includes requests for quotes, contracts, treaties, business notices, meetings, conferences, etc.
From this perspective, national/inter-organizational and international communication are also subcategories of external communication.
(a) National/Inter-organizational communication:
National or inter-organizational communication refers to communication between various organizations within the same nation. An example of this kind of communication occurs between ABC Boarding School, Kathmandu, and XYZ Public School, Biratnagar.
(b) International communication:
International communication refers to interactions between businesses based in various nations. This kind of communication, which took place between Oxford University London and Hamro International School, Jawalakhel, is an example.
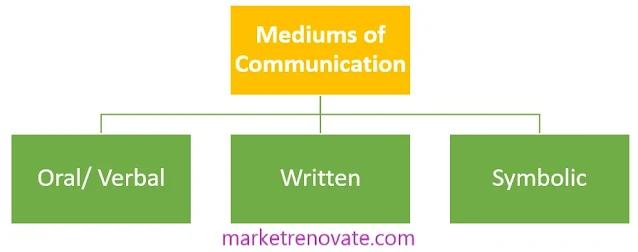
Mediums and means of communication
The office uses a variety of channels and tools to transmit and relay information between people and organizations, taking into account its resources and financial situation. Communications are conducted internally and externally using a variety of channels and methods. "Mediums" are the means or procedures used to transmit information. Similar to this, "means" refers to the tools or equipment used in communication.
The chart displays the various communication forms, and each explanation is provided below:
A. Oral/Verbal Communication
When something is spoken, whether face-to-face or through a phone, cell phone, or another device, it is said to be oral or verbal communication. For example, internal communications between various staff members and departments are typically conducted orally. Under this medium, an immediate response can be attained. It thus saves time. The following are some notable oral communication techniques:
Man/Messenger:
The familiar, organic, and conventional form of communication is the man/messenger. For the instruction of executives, the office appoints messengers or peons to deliver messages and documents between sections and departments as well as to parties outside the company. Facial contact during face-to-face conversations, personal interviews, meetings, conferences, discussions, and in-class instruction are examples of person-to-person communication.
Telephone:
The telephone is a widespread and well-liked oral communication method today. It is a mechanical device that transmits oral messages from one person to another far away or closes using wire connection systems or wave signals. It is the simplest, most practical, and most efficient form of communicThisgh this makes it simple for us to communicate with people anywhere on the planet. Wave phones and cellular postpaid and prepaid phone services have been introduced in our nation.
Loudspeaker:
It is a tool for widespread communication. It is specifically used to openly communicate information, notices, and messages to a sizable audience. For example, it is used to announce messages or deliver speeches in large gatherings, conferences, airports, railway stations, bus stations, factories, schools, religious programs, film theaters, etc.
Radio and Television:
In urban and rural areas, radio and television is the most widely used form of oral/verbal communication. Both private and public institutions use these channels to disseminate public announcements and product advertisements.
Dictaphone:
In large and sophisticated offices, a device resembling a tape recorder is used to transmit verbal messages, called a dictaphone. The chief or executives record the necessary messages, instructions, and data when pressed for time or when there is no P.A. Later, the assistant turns on the dictaphone and listens to the recorded instructions.
Picture phone:
A picture phone is a phone with a display. When they are conversing, it enables its users to see one another. The telephone set's built-in visual screen makes it possible. By definition, a picture phone displays the image of the person speaking on its display. They can even express themselves through facial expressions, thanks to it.
Intercom system
In large organizations, the Inter-com system, which enables the communication between various departments and sections within the organization, is very well-liked. A phone line is not needed for the intercom system. One can speak with another department by dialing the specific number designated for each department or section on a telephone. The EPABX communication method is made possible through an electronic device.
Speaking Tube or Voice Pipe:
It is a system that uses two cones joined by an air pipe to transmit speech over a considerable distance. The majority of the time, it was utilized for shipboard communications. The 19th century saw the application of the principle in luxurious residences, offices, fine cars, military aircraft, and even locomotives. The speaking tube was eventually phased out in favor of the telephone. This item was also referred to as a "megaphone."
B. Written Communication:
Sending information, orders, instructions, and messages via written means—such as a letter, telegram, telex, fax, e-mail, the internet, etc.—is written communication. It is an official, trustworthy method of communication. As a result, it can be consulted or used as evidence as needed in the future. The following are some common forms of written communication:
Correspondence:
It is a typical, convenient, affordable, and reliable method of written communication. It is the act of writing a letter, notice, or circular to convey information to various sections and departments internally and externally, i.e., outside the organization. Additionally, we frequently use it to send private messages to our friends, family, and loved ones.
Fax:
A fax is an electronic device. Through radio waves or a telephone connection, it is used to transmit written and printed documents, photographs, drawings, etc. This system requires that both the sender and the recipient have access to similar fax machines. Senders should use the fax number just like the phone number when sending written correspondence. The sender should then put the written document into their fax machine by feeding it in or inserting it. The fax machine reads it and transmits an exact document copy to the recipient's fax machine. It is a time-efficient and trustworthy method of written communication.
E-mail/Electronic mail:
It is a network of computers connected by electronic gadgets. Nowadays, using a phone connection to send and receive written messages through computers is very common. To send and receive written communication, a computer must be configured with a specific e-mail address. An example of an e-mail address is gpsir@marketrenovate.com.np. E-mail messages must be typed into a computer and sent to the recipient's e-mail address to be sent. It is a less expensive, quicker, and more straightforward method of communication.
Internet/International network:
It is an extensive computer network that spans the entire world. Telephone lines, satellite systems, microwave channels, and cable lines connect computers. It consists of information hubs, or websites, where people gather and use information worldwide. For example, websites are where an organization's information is published online or its code address. It is currently the most cutting-edge and contemporary form of communication.
Telegram:
It is a method of transmitting information over wires and wireless systems using electrical pulses. It is primarily used in places with no other communication options, such as telephone, e-mail, internet, etc. Only brief information is sent using this system due to the cost. The message from the sender should be written down along with the recipient's name and address. It is then delivered to the telegram office. The same message is sent to the recipient by the telegram office. Every district of our nation has access to this service.
Telex:
A mechanical device that resembles a typewriter is called a telex. It is a form of written communication. It is specifically used to send lengthy messages to people or offices abroad. The desired telex code number and a signaling button are pressed when the message is ready to be transmitted. The message is typed and printed on the receiving device after that. This service can be set up by renting a teleprinter from Telecommunication Corporation.
Tele-printer:
A teleprinter is a two-part electronic gadget. The electronic typewriter with a standard keyboard is one of the teleprinters, and it may or may not have a memory to store messages before they are transmitted. The component of a teleprinter that points to the message is the opposite of a typewriter with no keyboard. At the receiving end, an automatic electromagnetic transfer process prints the message typed on the typewriter at the transmission center. As a result, it is a written form of communication.
E-fax:
Sending written information and documents using a fax machine and a computer's network operating system is prevalent. The computers connect to another computer, unlike e-mail. However, the two devices—a computer with an e-mail address and a fax machine—are connected at their opposite ends by a phone line or radio waves. Information is entered into computers and sent to another person's fax machine at the appropriate fax number. The received end receives the transmitted information in printed form. As a result, electronic faxing helps send printed documents. Additionally, digital drawings can be sent via fax.
C. Symbolic Communication:
It alludes to transmitting information using various signals, symbols, and gestures. According to the circumstance and type of information, symbolic communication is a crucial form of communication. Color, bell, symbol, and light can all be used to communicate symbolically. For instance, a school may use colorful flags, a traffic police station may employ a variety of lights and symbols, and a driver may employ lights and signs.


.jpeg)
0 Comments
If this article has helped you, please leave a comment.