Final Population Data of Nepal 2078 B.S/ 2021 A.D Made Public
Kathmandu, 24 March 2079: Today, the final results of the 2078 B.S./ 2021 A.D National Population Census are made public. In a ceremony held at Soaltee Hotel, Prime Minister Pushpa Kamal Dahal revealed the final results of the 2078 National Population Census.
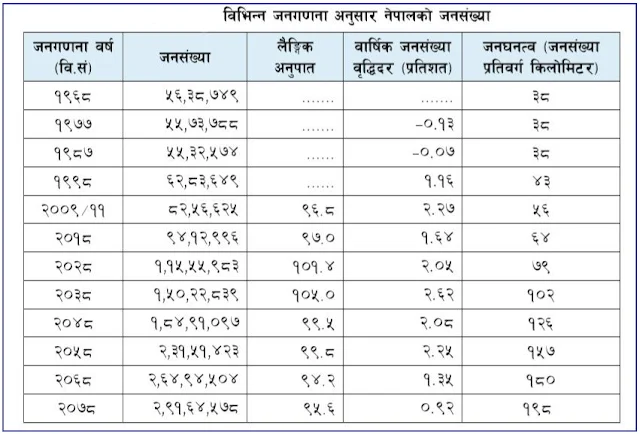
According to the National Population Census of 2078 (Reference Day for the Census: Mangsir 7, 2078), the population of Nepal is 2,91,64,578. Of which there are 1 crore 42 lakh 53 thousand 551 males (48.98 percent) and 1 crore 49 lakh 11 thousand 27 females (51.02 percent). Therefore, the gender ratio, or the number of women to one hundred men, is 95.59.
According to the most recent census in 2068, the population was 2,64,94,504, and the gender ratio was 94.16.
The National Planning Association gathered the 2078 census from 25th Kartik to 9th Mangsir 2078 for the Statistics Department. Last year, the preliminary results were made public in Magh. According to the preliminary report, the total population was 2,91,92,480. Nepal conducts a national population census once every 10 years.
According to the National Census of 2078, the number of other genders (sexual minorities) is 2,092 individuals, or 0.01 percent of the total population.
The average annual growth rate of the population throughout the census period is 0.92 percent per year, compared to 1.35 percent per year in the 2068 census.
According to the district-by-district research, Bhaktapur district had the highest average annual population growth (3.35 percent), while Ramechhap district had the lowest average annual population growth (1.67 percent).
The population density (population per square kilometer) is 198 people per square kilometer, compared to 180 people per square kilometer in 2068.
The population density in the Terai region is 460 people per square kilometer, whereas the population density in the mountains is 34 people per square kilometer. The most populous district is Kathmandu (5,169 inhabitants per square kilometer), and the least populous is Manang (3 people per square km).
According to the 2078 Census, there are 66 lakh and 66 thousand 937 families living in the country. Of which there are 66 lakh, 60 thousand 84 individual families, and 6 thousand 96 institutional families. The average household size has decreased to 4.37 persons from 4.88 members in 2068.
According to the 2078 census, Bagmati Province has the largest population. Bagmati province includes 20.97% of the total population or 61,20,000 people. After then, the population of Madhesh province is 61 lakh 10 thousand. Karnali is the province with the smallest population. 5.79 percent of the total population resides in Karnali.
In 2078, the average number of family members in the Himalayas is 4.33; in the mountains, it is 3.99, and in the Terai, it is 4.73. Family size is greatest in the district of Rautahat (5.94) and lowest in the districts of Gorkha and Dolakha (3.49). The total number of families in the 2068 census was 54 lakh 27 thousand 302.
Source: CBS, 2023
According to the 2078 census, the rural municipality is home to 66.1% of the people, while the urban municipality is home to 33.8%. According to the 2068 census, 63.19 percent of the population resided in rural areas, while 36.81 percent resided in urban municipalities.
53.61 percent of the total population (1 crore 56 lakh 34 thousand six people) resides in Terai, 40.31 percent (1 crore 17 lakh 57 thousand 624 people) in the mountains, and 6.08 percent (17 lakh 72 thousand 948 people) in the Himalayas.
Regarding population distribution among the provinces, Bagmati province has the highest population at 20.97%, while Karnali province has the lowest population at 5.79%. Kathmandu is the most populous district in Nepal, with 41,587 people, while Manang is the least populous (5 thousand 658 people).
Economically Inactive Population of Nepal According to Census 2078 Final Data
The number of Nepalis living without work or looking for work has risen to 82 lakh 11 thousand 12. This represents 34.3 percent of the 2 billion 39 million 58 thousand 868 economically active people. According to the public results of the National Census 078 released on Friday, 39.5 percent of women and 28.6 percent of men in Nepal are economically inactive among people aged 10 and up (economically active).
In Madhesh, 22 lakh 19 thousand 567 people (46.5 percent) are economically inactive. Following that, it was discovered that 20 lakh 13 thousand 995 Bagmati residents were not engaged in any financial work. “The majority of them, 46.9 percent, are not working because they are students,” according to the Census data booklet, “and they are not working financially due to household chores, family care, old age, disability/sickness, and other reasons.”
Nepal has 42 lakh 63 thousand students, according to census results. The number of people who are only allowed to do housework and no outdoor financial work is 19 lakh 67 thousand 486, or 21.9 percent. 11 Percent of people do not work economically because of old age, and 7.5 percent are family caregivers. The disability/sickness rate is 2.5 percent, and the pension/disability rate is 2.2 percent.
People aged 10 and up who have done any economic work for any period or are looking for any economic work are included in the economically active population at the time of the census. Persons who did no economic work and did not seek economic work during the reference period are classified as inactive.
It was discovered that 93.05 percent of the 1 crore 270 thousand 447 are frequently economically active, while 6.95 percent are frequently unemployed. The total number of people engaged in economic work is 14,983,310. Agriculture is the economic occupation most or half of the country’s population chooses. According to the census, the country has 50.1 percent of skilled agriculture, forestry, and fisheries workers.
Following this, it was found that 23% of general or primary occupation workers, 5.6 % of service and goods sales workers, and 5.1 % of managers. Even when economic work is classified by industrial sector, agriculture, forestry, and fisheries employ 85 lakh 86 thousand people.
Because agriculture provides a living for half of the country’s population, the government has been slow to promote this industry. Farmers have not received adequate services such as fertilizers, seeds, technology, irrigation, subsidized loans, and the pricing of produced goods. 55.3 percent of those who worked economically during the census reference period were self-employed. This means 82 lakh, 92 thousand 45 people in Nepal are economically active and own businesses. Looking at the provinces, Karnali has the highest proportion of self-employed people (65.6%), while Madhesh has the lowest (49%).
Self-employment affects 59% of women and 52% of men. There are 42 lakh 92 thousand job seekers in the country. 34.7 percent are male, while 21.9 percent are female. Two hundred and twelve thousand people have found work. There are 21 lakh 75 thousand 380 people who assist the family financially.
When considering the institutional sector of economic work, the household sector employs the greatest number of people, 92 lakh 60 thousand, or 61.8 percent. In Nepal, 32.7 percent of people work in non-profit organizations, and 3.9 percent work for the government. Financial institutions employ 1.1 percent of the workforce, or 1 lakh 63 thousand people. The country’s total population is 2 crore, 91 lakh, 64 thousand 578 people. Of which 1 crore 49 lakh 11 thousand 27 (51.02 percent) are women and 1 crore 42 lakh 53 thousand 551 are men (48.98 percent).
Although Nepal is a multi-ethnic, multilingual, and multi-religious, the census excludes caste, language, and religion data. According to the National Statistics Office, the data will be released after four months due to disagreements over language and religion. Only the total population and gender ratio from the first national census conducted after the formation of the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal was made public.
Personal details of more than five years, including name, surname, caste/ethnicity, sex, birth certificate, age, ancestral language, mother tongue, second language, and religion, were requested under the slogan “My Census, My Participation.” However, caste, language, and religion statistics were not made public.
According to the 2068 census, the country had 125 castes, 123 languages, and 10 religious communities. If data on caste, language, and religion are not made public, the government at all three levels will be hampered in implementing upliftment and development programs for the target communities. The age group of 15 to 59 years accounts for 61.96 percent of the total population. This is a productive population. The population under 14 is 27.83 percent, while the population over 60 is 10.21 percent. The annual average population growth rate is 0.92 percent. The growth rate in the 2068 census was 1.35, which is 0.92 in 2078. The highest population growth rate is 3.35 percent in Bhaktapur, and the lowest is minus 1.67 percent in Ramechhap.
Number of Families According to Final Population Data of Census 2078
The total number of families is 66 lakh 66 thousand 937. The number of families has increased by 23% since the last census. Individual families number 66 lakh 60 thousand 841 while institutional families number 6 thousand 96. A typical family has 4 to 5 members. Mountains comprise 6.08 percent of the total population, or 17 lakh 72 thousand 948 people. The hills have 40.31 percent of the population (1 crore 17 lakh 57 thousand 624 people), and the plains have 53.61 percent (1 crore 56 lakh 34 thousand 6 people).
Provincial Population Distribution According to Final Population Data of Census 2078
The population of Koshi province is 17.01 percent, Madhesh province is 20.97 percent, and Bagmati province is 20.97 percent. Similarly, the population of Gandaki province is 8.46 percent, that of Lumbini province is 17.56 percent, that of Karnali province is 5.79 percent, and that of Sudurpaschim province is 9.24 percent. There are 293 and 460 rural municipalities in the country’s 753 local levels. The municipality’s population is 66.17 percent and 33.83 percent in the rural municipality. The population of Kathmandu metropolis is 862,400, while the population of Thulieveri municipality is 9,861. Similarly, Baijnath Rural Municipality has the highest population of 69,472 and Narpabhumi Rural Municipality has the lowest population of 396.
Population Living Abroad According to Final Population Data of Census 2078
21 lakh 90 thousand 592 people are working and studying abroad. 82.2 percent are men, while 17.8 percent are women. There is no information on those who have left the country. The number of Nepalese who have been separated from their families has increased by 269,098 in the last ten years. According to Census 2078 data released on Friday, 21 lakh 90 thousand 592 people from 15 lakh 55 thousand 961 families are absent and frequently live abroad.
There were 17,99,675 men (82.2 percent) and 3,90,917 women (17.8 percent). According to the census of 2068, 19 lakh 21 thousand 494 people were away from their families and frequently lived abroad.
Population Growth Rate According to Final Population Data of Census 2078
The population growth rate in 34 districts is negative. Ramechhap, Khotang, Manang, Bhojpur, Tehrathum, Syangja, Gulmi, Acham, Parbat, Arghakhanchi, Panchthar, Sindhupalchok, Dhankuta, Dolakha, Gorkha, Baglung, and Lamjung are among them. Similarly, the population growth rate in Palpa, Myagdi, Okhaldhunga, Taplejung, Nuwakot, Kavrepalanchok, Ilam, Dailekh, Baitadi, Doti, Dhading, Bajhang, Dadeldhura, Salyan, Solukhumbu, Tanahun, and Sankhuwasabha is negative. The National Population growth rate is 0.92% Per Annum. This indicates it will take approximately 76 years to double Nepal’s population.
Demographic Measures According to Final Population Data of Census 2078
The maternal and infant mortality rate is 151 per 100,000. Twelve percent of married women between 15 and 49 have had a stillborn child. 12 percent (7 lakh 36 thousand 499) of 61 lakh 45 thousand 39 married women aged 15-49 had a stillborn child. The proportion of married women giving birth to two live babies is 33%, while the proportion of women giving birth to one live baby is 23.1 percent. According to census data, “a total of 61 lakh 45 thousand 39 married women aged 15-49 have given birth to 127 lakh 99 thousand 69 children so far, of which 52.7 percent are sons and 47.3 percent are daughters.” 3.2 percent of all live births died. Boys comprise 57.6 percent of dead infants, while girls comprise 42.4 percent.
Women constitute 31.55 percent of the 66 lakh 66 thousand 937 families. The census results show a 5.82 percent increase from 2068. 86 percent of all families own their own homes. Wood/firewood is used by 51% of all families for cooking. 92.2 percent of households use electricity. 57 percent use tap/pipe, 29.8 percent tubewell/hand pump, 1.5 percent well/well, 3.9 percent mains water, and 4.6 percent jar/bottle water. 95.5 percent used the toilet.
Literacy and Education According to Final Population Data of Census 2078
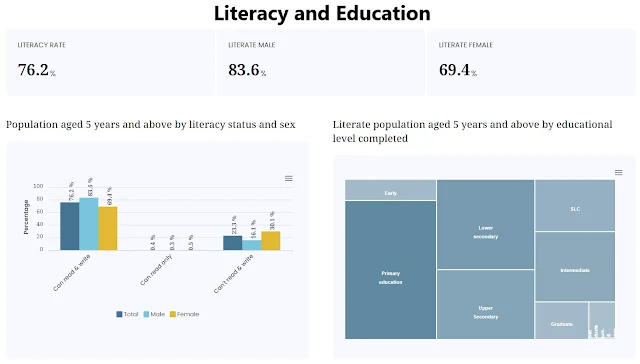
Nepal’s overall literacy rate has increased to 76.3 percent. The male literacy rate is 83.6 percent, and the female literacy rate is 69.4 percent. The literacy rate in the 2068 census was 65.9 percent.
The majority of Nepalese higher education students are interested in the management field. According to the final results of the National Census-2078, the majority of people, 35.1 percent, have studied the management field. People who studied Education come in second with 29.9 percent, followed by people who studied humanities and social sciences with 11.5 percent.
Those studying Science, Health/Medicine, Engineering, Computer/Information Technology, Law, Agriculture, Forestry, and Animal Science/Veterinary/Fisheries account for 7.1 percent, 4.4 percent, 3.0 percent, 1.2 percent, and 0 percent, respectively.
At least 19.5 percent of the population is 12th Pass. When gender is considered, the majority of males (36.9%) have studied management, while the majority of females (36.1%) have studied pedagogy. Women and men study humanities and social sciences equally (11.6%).
Smartphones and Personal Vehicle Users According to Final Population Data of Census 2078
In Nepal, smartphones are available to 73% of the population. According to the results of the National Census 2078, released on Friday, 73 percent of Nepalese people own a smart mobile phone. Ordinary mobile phones are available to 73.2 percent of the population.
A question with 14 options, including radio, television, landline, mobile phone, computer, internet, and vehicle, was asked in the census to collect information about the facilities and services available to every family in the country. According to the data, 3.9 percent of families do not have any facility, while 96.1 percent have access to some kind of equipment.
According to the report, only 49.4 percent of Nepalese have access to television, while 34.2 percent listen to the radio. 15 percent of Nepalese own a computer, and 37.8 percent have Internet access.
Sexual and gender minorities According to Final Population Data of Census 2078
According to census data, there are 2 thousand 928 people of gender and minorities in the country. This represents 0.001% of the total population. Wagmati province has the highest percentage (32.7%), and Karnali province has the lowest (2.8%).
Some form of disability affects 2.2 percent of the total population. Based on the total population, 2.5 percent of men and 2% of women have disabilities, according to the census. There are 351 thousand 301 men and 293 thousand 443 women among them. The census questionnaire mentions twelve different types of disabilities. Physical disabilities include low vision, total blindness, deafness, hearing loss, hearing impairment, voice and speech, mental or psychosocial disabilities, intellectual disabilities, hereditary bleeding (hemophilia), autism, and multiple disabilities.
The census results do not include any information about refugees. During the census, those who had obtained the refugee identity card refused to give it up, claiming that the Nepalese government had not assisted them, so why should they? Tibetans and other refugees have been living in Kathmandu Valley’s Swayambhu, Buddhist, and Kantakuna districts.
No Information Regarding Lipulek in the latest Census 2078
It is connected to Changru and Tinker of Vyas Rural Municipality-1 of Mahakalipari Darchula, Kalapani and Lipulek lands. The census was not conducted in that area after 2018. Despite the government’s introduction of the new ‘Chuchche map’ of Nepal, houses and households could not be listed in the Kalapani and Lipulek areas beyond Mahakali, which are included in the Beaked (Chuchche) map. According to the National Statistics Office, traveling through India is required to reach the area. The Indian Armed Police Border Outpost (BOP) refused to allow the representative to collect census data.
LP Gas Cylinder Users According to Final Population Data of Census 2078
In the last ten years, the number of families using gas for cooking has increased. According to the National Census 2078, 44.3 percent of families cook with LP gas, released on Friday. According to the National Census 2068, approximately 30% of families used LP gas.
According to the census of 2078, most LP gas users live in Bagmati province. Gas is used by 69 percent of Bagmati’s families (10 lakh, 94 thousand 195). Similarly, 51.1 percent of Gandaki families and 42.2 percent of Lumbini families use LP gas. Karnali province uses the least amount of gas. According to the Census 2078 report, only 16.9 percent of Karnali families use gas.
3% of children are separated from their parents
According to statistics, 3% of Nepalese children are forced to live apart from both of their parents. According to the twelfth national census results in 2078, there are 9,869,583 children under eighteen. Three percent of these children are not living with both parents.
Both parents live with their children in 77.9% of cases. The percentage of children who live solely with their mother is 17.1%, while the percentage of children who live solely with their father is 1%. Some children who have been separated from their parents live with relatives or relatives, while others work in hazardous and domestic labor.
Key Results of National Population Census of Nepal Final Report 2021/ 2078 B.S
1. Population:
The total population of Nepal as of the census day (November 25, 2021) is 29,164,578, with 14,253,551 males (48.98%) and 14,911,027 females (51.02%). As a result, the sex ratio is 95.59 males for every 100 females. In 2011, the total population was 26,494,504, with a male-to-female ratio of 94.16.
2. Population of other genders:
In the first phase of census fieldwork in 2021, information about the total number of males, females, and ‘other gender’ (sexual and gender minorities) usually living in households was collected using the house and household listing form. As a result, 2,928 people (0.01 percent of the total population) are classified as ‘other gender.’
However, in the main questionnaire, the details of the individuals from this community were classified as male or female based on their biological sex. The highest number (32.7%) of those who reported as ‘other gender’ are in Bagmati province, while the lowest (2.8%) are in Karnali province. In Madhesh, Lumbini, Koshi, Gandaki, and Sudur Pashchim provinces, this community accounts for 24.9, 14.8, 10.4, 7.8, and 6.8 percent of the total ‘other gender’ population.
3. Annual average population growth rate:
According to Census 2021, the annual average population growth rate is 0.92 percent. In 2011, this rate was 1.35 percent. Bhaktapur has the highest annual average population growth rate (3.35%), while Ramechhap has the lowest (-1.67%).
4. Population density:
In 2021, the population density (number of people per square kilometer of area) is 198, up from 180 in 2011. The Tarai region has the highest population density (460), and the Mountain region has the lowest (34). Kathmandu district has the highest population density (5,169), while Manang district has the lowest (3).
5. Population by broad age group:
According to the 2021 census, 61.96 percent of Nepal’s total population is between the ages of 15 and 59. In 2011, this age group made up 56.96 percent of the population. Currently, 27.83 percent of the population is 14 years or younger, and 10.21 percent is 60 years or older.
6. Households:
The total number of households has increased by 23 percent, from 5,427,302 in 2011 to 6,666,937 in 2021. In 2021, the total number of conventional (non-institutional) households will be 6,660,841, up from 5,423,297 in 2011.
7. Average household size:
According to the 2021 census, the average household size is 4.37 people, up from 4.88 in 2011. According to the ecological belt, the average household size in the Mountain region is 4.33 people, 3.99 in the Hill region, and 4.73 in the Tarai region. The average household size in the Rautahat district is 5.94, while it is 3.49 in Gorkha and Dolakha districts.
8. Population of urban and rural municipalities:
According to the 2021 census, the population of urban municipalities reached 66.17 percent, while the population of rural municipalities reached 33.83 percent. The population in urban and rural municipalities was 63.19 percent and 36.81 percent, respectively, after reallocating the 2011 census population according to the federal structure. The sex ratio of the population in urban municipalities was 95.89 in 2011, but it remained at 96.06 in 2021, while it has increased from 91.27 to 95.59 in rural municipalities.
9. Highest and lowest population districts:
Kathmandu district has the highest population (2,041,587 people), and Manang district has the lowest population (5,658 people) of the country’s 77 districts. In that order, Morang, Rupandehi, Jhapa, and Sunsari are the second, third, fourth, and fifth most populous districts. Mustang, Dolpa, Rasuwa, and Humla are the second, third, fourth, and fifth most populous districts, in that order.
10. Population by ecological belt:
According to the 2021 census, the Tarai region has 53.61 percent (15,634,006 people), the Hill region has 40.31 percent (11,757,624 people), and the Mountain region has 6.08 percent (1,772,948 people). In the 2011 Census, the Tarai region had 50.27 percent (13,318,705 people), the Hill region had 43.01 percent (11,394,007 people), and the Mountain region had 6.73 percent (1,781,792 people).
11. Population distribution by province:
The population distribution by the province in 2021 shows that Bagmati province has the highest population share (20.97%), and Karnali province has the lowest (5.79%). Madhesh province has the second highest population. Similarly, in terms of population size in 2021, Koshi, Lumbini, Sudurpaschim, and Gandaki Provinces rank third, fourth, fifth, and sixth, respectively.
12. Number of building structures by main use:
In the 2021 census, all building structures in the country were counted for the first time. Building structures are classified into 12 different types based on their primary use. The primary use is the one for which the majority of the structure is designed.
There are a total of 75,52,066 building structures in the country, with 71.7 percent primarily used for residence, 10.1 percent for shed or storage, 6.3 percent vacant, 3.1 percent for business/trade, 1.1 percent for educational purposes, 0.4 percent for industry/manufacturing establishment, 0.4 percent for institutional use, 0.4 percent for government, 0.3 percent for hotel and lodge, 0.2 percent for health-related purposes, and 0.1 percent for banking and finance.
In Lumbini province, 75 percent of the buildings and 68 percent of the buildings in Sudur Pashchim province were used primarily for residential purposes.
13. Housing unit ownership:
In 2021, 86.0 percent of the total 6,660,841 conventional households resided in their own housing units, while 12.8 percent resided in rented housing units. The proportions of households residing in their own housing units and rented housing units in the 2011 census were 85.3 percent and 12.8 percent, respectively. According to the census of 2021, 0.6 percent of households reside in institutional housing units, while 0.7 percent reside in other types of housing units.
14. Primary source of drinking water:
According to the 2021 census, tap/piped water (inside and outside household premises combined) is the primary source of drinking water for 57.0 percent of all households (6,660,841). Other major sources of drinking water for households include well/hand pump (29.8%), jar/bottled water (4.6%), spout (3.9%), uncovered well/kuwa (2.1%), covered well/kuwa (1.5%), and river/stream (0.4%). According to the 2011 census, tap/piped water was the primary source of drinking water for 47.8 percent of total households (5,423,297), while tube well/hand pump was the primary source of drinking water for 35.1 percent of total households.
15. Primary source of cooking fuel:
According to the 2021 census, more than half (51%) of all households in the country use wood/firewood as their primary source of cooking fuel. Other major sources of cooking fuel include liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) 44.3%, cow dung 2.9%, biogas 1.2%, electricity 0.5%, kerosene 0.05% and other 0.1% of total households. According to the 2011 census, 64.0 percent of all households used wood/firewood for cooking.
16. Primary source of lighting:
According to the Census 2021, most households use electricity as their primary lighting source. The proportion of households that use electricity as their primary source of lighting has risen from 67.3 percent in 2011 to 92.2 percent in 2021. Other common lighting sources include solar energy (6.6%), kerosene (0.6%), and other sources (0.6% of households in 2021). In 2011, the percentages of households using kerosene, solar, and other lighting sources were 18.3, 7.4, and 6.1, respectively.
17. Household assets/amenities:
According to the 2021 census results, 3.88 percent of total households lack any household assets/amenities, while 96.12 percent of households have at least one household asset/amenity. Ordinary mobile phones are owned by 73.15 percent of households, while smart mobile phones are owned by 72.94 percent of households. Other assets/amenities available in households include an electric fan 53.1%, a television 49.37%, an internet facility 37.72%, a bicycle 35.21%, a motorcycle/scooter 27.3%, a refrigerator 23.7%, a computer/laptop 15%, a washing machine 4.2%, and a car/jeep/van 3.1%.
18. Toilet facility:
95.5 percent of the 6,660,841 conventional households (excluding institutional households) enumerated in the 2021 census use one or more types of toilet facilities, while 4.5 percent do not have access to any toilet facility. According to the 2011 census, 38.2 percent of households lacked toilet access.
19. Female house and land ownership:
Overall, 23.8 percent of total households own land or a housing unit or both (land & housing unit) in the name of a female household member. The percentage of households with female ownership of both land and housing unit is 11.8 percent, a 1.1 percent point increase from 2011.
20. Number of households running small-scale businesses other than agriculture:
According to census data, there are 6,27,887 (9.4%) households running small-scale businesses other than agriculture with no paid employees. Among such households, 137,644 (21.9%) run cottage industries, 310,651 (49.5%) trade/business, 34,656 (5.5%) run transportation, 69,177 (11%) run service-related businesses, 75,559 (12%) run other types of such small-scale enterprises in the country, with men running 55 percent and women running 45 percent. The provinces with the highest and lowest numbers of such enterprises are Bagmati (153,522 (24.5%) and Karnali (32,463 (5.2%) households, respectively.
21. Population of absentees abroad:
According to the 2021 census, a total of 2,190,592 people from 1,555,961 households (23.4%) are absent and living abroad. The total number of absentees living abroad is 1,799,675 (82.2%) male and 390,917 (17.8%) female. In 2011, 1,921,494 people from 1,378,678 (25.4%) households were absent abroad, with males accounting for 87.6% and females accounting for 12.4%.
22. Female household head:
Overall, 31.55 percent of total households (6,666,937) are headed by a woman, a 5.82 percent increase since 2011.
23. Marital status:
According to the 2021 census, 33.1 percent of the total population aged 10 and up has never married. Unmarried men account for 38.2 percent of all males and 28.4 percent of all females aged 10 and up. Similarly, 61.8 percent of the total population aged 10 and up is married, while 4.5 percent is a widow/widower. By gender, 59.1 percent of males and 64.3 percent of females in this age group are married.
24. Age at first marriage:
According to the 2021 census, 34.4 percent (Male: 32.6% and Female: 35.9%) of the ever-married population aged 10 and up married between the ages of 18 and 20. Similarly, 22.3 percent (Male: 12.3%; Female: 30.4%) of them married for the first time between the ages of 15 and 17. Furthermore, 7% (Male: 3.0% and Female: 10.2%) of them married for the first time between the ages of 10 and 14 years. Some of them (0.3%) married for the first time before reaching the age of ten. The average age at first marriage is 19 years. The average age at first marriage is 21 years for men and 18 years for women.
25. Disability:
According to the 2021 census, 2.2 percent of the total population has one or more types of disabilities. Males account for 54.2 percent of all disabled people, while females account for 45.8 percent. According to the 2011 Census, 1.94 percent of the total population had one or more types of disabilities.
26. Literacy rate:
According to the 2021 census, the literacy rate of the country’s total population aged 5 and up is 76.3 percent. The male literacy rate is 83.6 percent, while the female literacy rate is 69.4 percent. According to the 2011 census, the overall literacy rate was 65.9 percent, with male literacy at 75.1 percent and female literacy at 57.4 percent.
27. Education level attained:
Most (28.7%) of the literate population has completed primary school (classes 1–5). Similarly, 19.9 percent of the total literate population has completed lower secondary level (class 6–8), with 9.5 percent having completed S.L.C. (or equivalent). Similarly, 19.5 percent have completed higher levels of education (above S.L.C. or equivalent).
28. Population by place of birth:
69 percent of the total population has their birthplace and current residence in the same municipality. The current residence is the birthplace of 78.3 percent of males and 60 percent of females. Overall, 9% of the total population was born in a municipality other than the district of current residence, 19.5 percent was born in another district, and 2.5 percent was born abroad.
29. Population by former place of residence for current migration:
In total, 68 percent of the population has their usual place of former residence in the same location where they were enumerated. This equates to 77.0 percent for men and 59.4 percent for women. On the other hand, 10.7 percent of the total population had their former usual place of residence in another municipality of the respective district, 18.2 percent had their former residence in another district, and 3.1 percent had their former residence abroad.
30. Population at the current place of residence by the duration of last migration:
Of the total 9,341,408 people who currently migrated, the d Similarly, 4.0 percent of total migrants have been displaced for more than 50 years. Similarly, in terms of sex, the duration of the last migration is 10-24 years for 29.1 percent of males and 33.3 percent of females.
31. Reasons for current migration:
Marriage accounts for 38.2 percent of all current migration. Work/job (15.2%), trade/business (2.8%), study/training (7.8%), dependent family member (19.5%), natural disaster (0.7%), agriculture (3.9%), returnee (4.1%), and other (6.6%) are the other reasons for current migration. By gender, 30.6 percent of male migrants migrated for work/jobs, while 58.2 percent of female migrants migrated for marriage.
32. Fertility status (children Ever Born):
According to the 2021 census, 12.0 percent of all ever-married women aged 15-49 (6,145,039) do not have any children. The percentage of ever-married women aged 15-49 who have had two children is the highest, at 33%. Similarly, 23.1 percent of all ever-married women aged 15-49 have had one child, while 0.1 percent of women have had nine or more children.
As of the census date, a total of 6,145,039 ever-married women aged 15-49 had given birth to 12,799,969 children. Males account for 52.7 percent of all children born, while females account for 47.3 percent.
According to the data, 3.2 percent of all children born alive have died. Males make up 57.6 percent of the children who died, while females make up 42.4 percent.
33. Current fertility:
A total of 412,935 children were born in the 12 months preceding the census, with males accounting for 218,074 (52.8%) and females accounting for 194,861 (47.2%). Among all children born in the 12 months preceding the census, 36.8 percent were born to women aged 20-24 years.
34. Maternal mortality:
According to the National Population Census 2021, 653 (5 percent) of the total 12,976 female deaths from the fertility age group (15-49 years) in the last 12 months preceding the day of enumeration were related to pregnancy. Verbal autopsies conducted in collaboration with the Ministry of Health and Population revealed that 622 (95 percent) of pregnancy-related deaths were caused by maternal mortality. During the same period, 412,935 live babies were born from the same age group of mothers. The maternal mortality ratio is 151, according to this (a total of 151 deaths of mothers per 100 thousand live births).
35. Children’s living arrangements:
Of the total 9,869,583 children (people under 18), 77.9% live with both parents (father and mother), 17.1% live with their mother, 1% live with their father, and 3% live with other relatives.
36. Duration of economic activities performed:
Of the 23,958,868 normally residing population in the country aged 10 years or older, 14,983,310 were engaged in any economic activity in the 12 months preceding the census. According to census data, 41 percent of people aged 10 and up worked for 6 months or more, 21.5 percent worked for less than 6 months, and 37.5 percent did not work during the reference period.
37. Economically active population:
Persons aged 10 and up who either performed any economic work for any length of time, regardless of whether they searched for work or not, or searched for work (part-time or full-time) if they had not performed any economic work in the previous 12 months preceding the census.
Persons who did not perform any economic work or look for work during the reference period are classified as economically inactive. Based on the above criteria, 15,689,777 people (65.5 percent) are classified as economically active, 8,211,012 people (34.3 percent) are classified as not economically active, and 58,079 people did not report their status.
38. Usually economically active population:
If a person’s total number of months actually worked and looked for work is greater than or equal to six months, the person is classified as usually economically active. On the other hand, a person with fewer than 6 months falls into the non-typically economically active population. According to this classification, 11,038,105 people (70.35 percent) of the total 15,689,777 economically active population are usually economically active, while 4,651,672 people (29.65 percent) are not usually economically active.
39. Usually employed population:
Among the total usually, economically active population, the usually employed population refers to those people whose working time is equal to or greater than their time off, whereas the usually unemployed population refers to those whose working time is less than their time off. According to the census of 2021, of the total 11,038,105 usually economically active population, 10,270,447 (93.05 percent) are usually employed, while 767,658 (6.95 percent) are usually unemployed.
40. Economically active population by the main occupation:
Among 14,983,310 people engaged in any economic activity during the reference period, agriculture, forestry, and fishery skilled workers have the highest share of people (50.1%), followed by elementary workers (23.0%), service and sales workers (5.8%), crafts and trade workers (5.6%), managers (5.1%), professionals (3.8%), plant and machine operators (2.7%), technician and associate professionals (1.7%). The occupation is classified using the Nepal Standard Classification of Occupations (NSOC).
41. Population economically active by main industry:
The Nepal Standard Industrial Classification of all economic activities has been used to code the industrial division of economic activities (NSIC). Agriculture, forestry, and fishing (57.3%); wholesale and retail trade, repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles (12.5%); construction (8.1%); other service activities (3.9%), and manufacturing (3.8%) were the top five industries among 14,983,310 people engaged in any economic activity in the 12 months preceding the census.
42. Employment status of economically active population:
Of the 14,983,310 people aged 10 and up who performed any economic work in the 12 months preceding the census, the highest proportion worked as own account workers (55.3%), followed by employees (28.6%), contributing family members (14.5%), and employers (1.4%). Similarly, 0.1% of the population has not stated their employment status.
43. Economically active population by institutional sector:
The household sector accounts for 61.8 percent of the 14,983,310 people who worked in the 12 months preceding the census. This is followed by non-financial corporations, governments, financial corporations, and non-profit institutions that serve households, with 32.7%, 3.9%, 1.1%, and 0.4%, respectively. While 0.1% of respondents have not specified their institutional sector.
44. Reasons for not being economically active:
Of those aged 10 and up who were economically inactive (i.e., did not perform any economic work), 46.9 percent cited being a “student” as the primary reason for not working. Household chores (21.9%), the elderly (11.0%), family care (7.5%), disability/illness (2.5%), pensions (2.2%), social work/volunteer service (0.3%), and other reasons (7.4%).
45. Birth registration status of children aged 5 and under:
Of the 30,07,648 children aged 5 and under, 74% have registered their birth, while 26% remain unregistered. Male children outnumber females by 5.8 percentage points among registered children. Similarly, the registration rate in Mountain is 81.9%, Hill is 73.1%, and Tarai is 73.7%. Karnali province has the highest percentage of registered children (87.3%), while Bagmati province has the lowest (67%).











.jpeg)
0 Comments
If this article has helped you, please leave a comment.